1、Concept of COB
COB, which stands for “Chip On Board,” is an electronic packaging technology where light-emitting chips are directly mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). They are adhered using conductive or non-conductive adhesives, followed by wire bonding for electrical connections, and then encapsulated with resin to protect the chips and bonding wires.

2、Differences Between COB and SMD
COB, like SMD, is a packaging method for LEDs. The difference lies in the fact that SMD is a surface-mount packaging technology, which involves soldering individual light cores onto the PCB to form a unit board. In contrast, COB integrates the light-emitting chips into the PCB itself, rather than soldering them onto the PCB one by one as with SMD.

SMD Display Screens
SMD display screens use solder to attach LEDs to the board, creating a raised structure. Each LED has only four small solder pads, making them susceptible to damage from pressure or contact during handling and installation, leading to dropped or dead lights. The small size of the solder pads also makes them prone to cold solder joints after SMT reflow soldering and can be easily knocked off, making their protectiveness relatively fragile. The delicate face mask is also susceptible to warping and deformation due to thermal expansion and contraction over time.
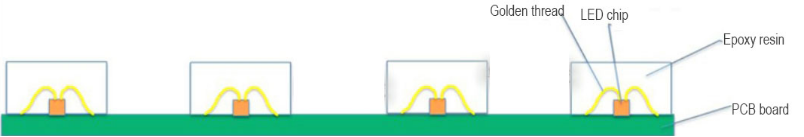
COB Integrated Packaging
COB integrated packaging encapsulates the light-emitting diode chips directly onto the PCB board with a lens on the surface, creating a smooth and flat surface that is more resistant to impact and wear. The screen surface can achieve an IP65 protection rating. The epoxy resin has a strong bond with the PCB board, ensuring that the LEDs are not damaged by external forces, making COB packaging highly resistant to external collisions. Therefore, COB packaged mini LED display technology has excellent protective capabilities.
3、COB Technology
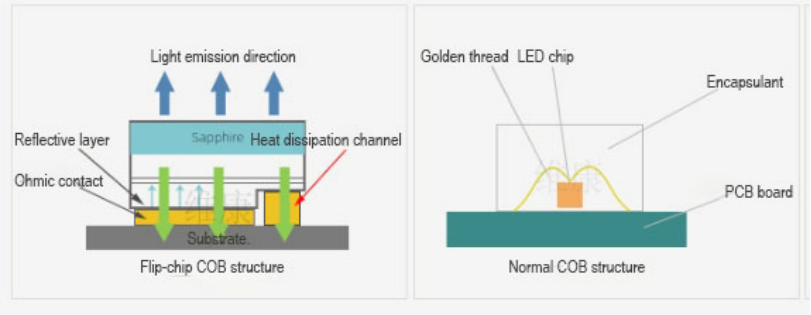
Normal COB and Flip-Chip COB
Normal Chip
A normal chip refers to a chip where the electrodes and the light-emitting surface are on the same side. The electrodes are connected to the substrate via metal wire bonding. This is a mature chip structure mainly used for LED screens with a pitch of 1.0 or above. The metal wires are primarily made of gold and copper, with a three-color LED light bead having five wires. It is susceptible to delamination due to humidity and stress, leading to dead lights.
Flip-Chip
A flip-chip has its light-emitting surface facing up and the electrode surface facing down, essentially the inverse of a normal chip, hence the name “flip-chip.” The advantages of flip-chip include no need for wire bonding, resulting in higher stability; higher light emission efficiency and lower power consumption; and a larger distance between the positive and negative electrodes, effectively reducing the risk of light bead failure.
4、Advantages and Disadvantages of COB
Advantages:
- COB, as a packaging process, encapsulates the light-emitting chips directly onto the PCB board. The device is fully sealed and not exposed, resulting in a hard and smooth screen surface, moving away from point light emission to achieve “surface light source” emission.
- High protection rating: Exposed devices are a significant drawback of SMD packaged LED displays, leading to dead or dropped lights. COB displays, however, use epoxy resin to solidify the light-emitting chips, fully sealing them. Therefore, COB displays are resistant to impact, and there is no concern about direct touch causing issues. They are also not susceptible to damage during transportation or installation, and environmental factors like outdoor moisture, oxidation, and lightning are effectively handled.
- Excellent viewing experience and image quality: A significant advantage of COB displays over LED small-pitch displays is the ability to surpass the physical limitations of SMD packaging, achieving smaller pitches. The increase in pixels per unit allows for more vibrant display images, coupled with COB displays’ ultra-high contrast ratio (10,000:1) and ultra-high refresh rate (>3840Hz), resulting in superior image quality. The “surface light source” emission principle effectively suppresses moiré patterns and reduces light refraction, concentrating the colors.
- Strong heat dissipation and low energy consumption: Due to the different packaging methods, COB displays are directly encapsulated on the PCB board, allowing heat to dissipate directly through the board without physical obstruction, leading to faster and more timely cooling. Moreover, COB displays consume 30% less energy than SMD packaged LED displays.
- Low dead light rate: Light repair is a common and tedious maintenance task for LED displays. COB displays fully seal the light-emitting chips, eliminating the possibility of light beads falling off or becoming loose, resulting in a widely acknowledge low dead light rate. However, some may question the difficulty of repair due to full sealing. This is a common misconception about COB displays: their strong protective capabilities mean that repairs are rarely needed. Even if repairs are necessary, they can be easily resolved with specific tools, and unlike SMD packaged LED displays, there are no visible repair marks after maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- High production difficulty: When packaging LED displays with COB, it is essential to ensure that each light is functioning correctly before encapsulation can proceed. This is different from SMD packaging, where individual light beads can be replaced. The process requires a high level of precision and skill, making it more challenging to produce.






